 This guide is designed to help patients aged 45 and older prepare for their first cardiac examination. Understanding what to expect during cardiac tests can alleviate anxiety. Each section covers a common cardiac test, including detailed procedures to follow, as well as the risks, contraindications, and post-procedure care. Always remember, consulting your healthcare provider for personalized advice is paramount.
This guide is designed to help patients aged 45 and older prepare for their first cardiac examination. Understanding what to expect during cardiac tests can alleviate anxiety. Each section covers a common cardiac test, including detailed procedures to follow, as well as the risks, contraindications, and post-procedure care. Always remember, consulting your healthcare provider for personalized advice is paramount.
Cardiac tests are essential tools that help healthcare providers assess your heart’s health. These tests can help identify issues, monitor existing conditions, and determine necessary treatments. Common cardiac tests include:
Each test has its own purpose and procedure. This guide will provide step-by-step instructions, common concerns, preparations needed, and aftercare recommendations.
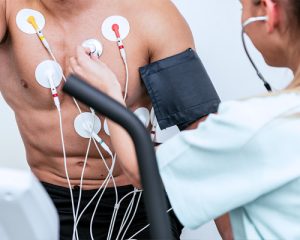
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of your heart. It helps detect heart problems like arrhythmias and other cardiac conditions.
The ECG procedure typically lasts about 10-15 minutes, with little to no waiting time involved.
There is no specific care required after an ECG. You can resume your normal activities immediately. However, if you experience any unusual symptoms, contact your healthcare provider.
ECGs are generally safe. However, patients with allergic reactions to adhesives should inform their provider. Rarely, some might experience skin irritation from the electrodes.
Patients often worry about discomfort from the electrodes or the pressure to stay still. Rest assured, the electrodes are painless, and the test duration is minimal.
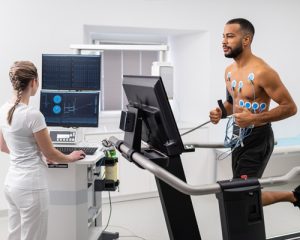
A stress test monitors the heart’s performance during physical exertion. This may involve walking on a treadmill or cycling while your heart rate and blood pressure are monitored.
The stress test usually takes 30-45 minutes, including prep and monitoring time, and might include a short waiting period for preparation.
After the test, rest for a few minutes while your heart rate normalizes. You may be advised to avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day, but otherwise, you can resume daily activities.
Stress tests are not recommended for individuals with severe heart conditions, recent heart attacks, or those who cannot exercise due to physical limitations. Discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before the test.
Patients may fear fatigue or discomfort during the exercise. It’s essential to know that you will be monitored closely, and you can stop at any time if needed.
An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create moving images of your heart. This test assesses heart structure and function, including the size of the chambers, condition of the valves, and overall heart function.
The entire echocardiogram takes about 45-60 minutes, with minimal waiting involved.
You can resume normal activities immediately. If the gel used during the procedure causes skin irritation, wash it off with soap and water.
Echocardiograms are very safe and have no known risks. The only contraindication might be for patients with severe allergies to ultrasound gel, which is rare.
Many patients are anxious about the ultrasound gel or the procedure itself, but the process is painless and non-invasive.
 Understanding cardiac testing procedures can empower you to approach your heart health with confidence. Remember the importance of consulting with your healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your specific health needs. Regular cardiac testing can lead to early detection and better management of potential heart conditions, ultimately improving your overall quality of life.
Understanding cardiac testing procedures can empower you to approach your heart health with confidence. Remember the importance of consulting with your healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your specific health needs. Regular cardiac testing can lead to early detection and better management of potential heart conditions, ultimately improving your overall quality of life.
For any concerns or questions regarding these procedures, please reach out to your healthcare provider before your appointment.